Checking an Array for Duplicate Values
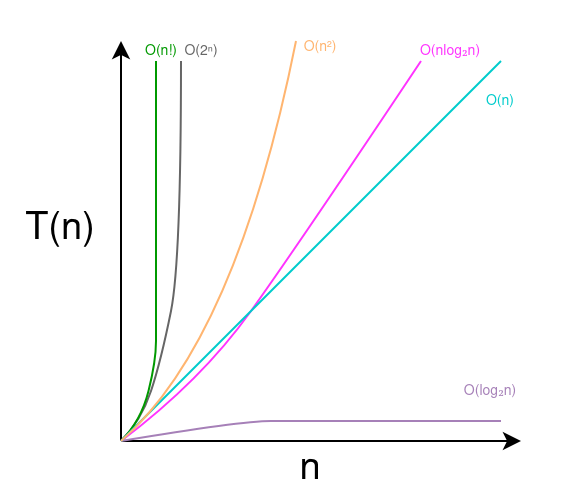
Problem Statement We have to implement a function containsDuplicate() that takes an integer array as input and returns true if an element occurs more than once and false otherwise. Brute Force Solution The simplest solution for this problem would be two nested loops, where the first loop will select an element and the second loop will select another element from the array and compare them. On the first occurrence of a duplicate element, the function will exit while returning true. ...